Trevelyan Wing, University of Cambridge
One year ago, Germany took its last three nuclear power stations offline. When it comes to energy, few events have baffled outsiders more.
In the face of climate change, calls to expedite the transition away from fossil fuels, and an energy crisis precipitated by Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Berlin’s move to quit nuclear before carbon-intensive energy sources like coal has attracted significant criticism. (Greta Thunberg prominently labelled it “a mistake”.)
This decision can only be understood in the context of post-war socio-political developments in Germany, where anti-nuclearism predated the public climate discourse.
From a 1971 West German bestseller evocatively titled Peaceably into Catastrophe: A Documentation of Nuclear Power Plants, to huge protests of hundreds of thousands – including the largest-ever demonstration seen in the West German capital Bonn – the anti-nuclear movement attracted national attention and widespread sympathy. It became a major political force well before even the Chernobyl disaster of 1986.
Its motivations included: a distrust of technocracy; ecological, environmental and safety fears; suspicions that nuclear energy could engender nuclear proliferation; and general opposition to concentrated power (especially after its extreme consolidation under the Nazi dictatorship).
Instead, activists championed what they regarded as safer, greener, and more accessible renewable alternatives like solar and wind, embracing their promise of greater self-sufficiency, community participation, and citizen empowerment (“energy democracy”).
This support for renewables was less about CO₂ and more aimed at resetting power relations (through decentralised, bottom-up generation rather than top-down production and distribution), protecting local ecosystems, and promoting peace in the context of the cold war.
Germany’s Energiewende
The contrast here with Thunberg’s latter-day Fridays for Future movement and its “listen to the experts” slogan is striking. The older activist generation deliberately rejected the mainstream expertise of the time, which then regarded centralised nuclear power as the future and mass deployment of distributed renewables as a pipe dream.
This earlier movement was instrumental in creating Germany’s Green Party – today the world’s most influential – which emerged in 1980 and first entered national government from 1998 to 2005 as junior partner to the Social Democrats. This “red-green” coalition banned new reactors, announced a shutdown of existing ones by 2022, and passed a raft of legislation supporting renewable energy.
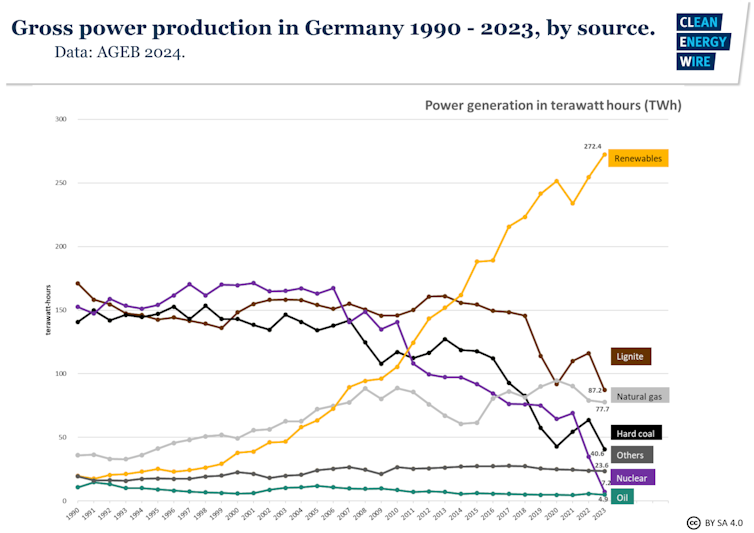
That, in turn, turbocharged the national deployment of renewables, which ballooned from 6.3% of gross domestic electricity consumption in 2000 to 51.8% in 2023.
These figures are all the more remarkable given the contributions of ordinary citizens. In 2019, they owned fully 40.4% (and over 50% in the early 2010s) of Germany’s total installed renewable power generation capacity, whether through community wind energy cooperatives, farm-based biogas installations, or household rooftop solar.
Most other countries’ more recent energy transitions have been attempts to achieve net-zero targets using whatever low-carbon technologies are available. Germany’s now-famous “Energiewende” (translated as “energy transition” or even “energy revolution”), however, has from its earlier inception sought to shift away from both carbon-intensive as well as nuclear energy to predominantly renewable alternatives.
Indeed, the very book credited with coining the term Energiewende in 1980 was, significantly, titled Energie-Wende: Growth and Prosperity Without Oil and Uranium and published by a think tank founded by anti-nuclear activists.
Consecutive German governments have, over the past two and a half decades, more or less hewed to this line. Angela Merkel’s pro-nuclear second cabinet (2009-13) was an initial exception.
That lasted until the 2011 Fukushima disaster, after which mass protests of 250,000 and a shock state election loss to the Greens forced that administration, too, to revert to the 2022 phaseout plan. Small wonder that so many politicians today are reluctant to reopen that particular Pandora’s box.
Another ongoing political headache is where to store the country’s nuclear waste, an issue Germany has never managed to solve. No community has consented to host such a facility, and those designated for this purpose have seen large-scale protests.
Instead, radioactive waste has been stored in temporary facilities close to existing reactors – no long-term solution.
Nuclear remains unpopular
National polls underscore the Teutonic aversion to nuclear. Even in 2022, at the height of the recent energy crisis, a survey found that 52% opposed constructing new reactors, though 78% supported a temporary extension of existing plants until summer 2023. The three-way Social Democratic-Green-Liberal coalition government ultimately compromised on mid-April 2023.
Today, 51.6% of Germans believe this was premature. However, a further deferral was deemed politically unfeasible given the trenchant anti-nuclearism of the Greens and sizeable cross sections of the population.
Despite some public protestations to the contrary (the main opposition CDU party declared in January that Germany “cannot do without the nuclear power option at present”), in private few political leaders think the country will, or even realistically can, reverse course.
As an industry insider told me, talk of reintroducing nuclear to Germany is “delusional” because investors were “burnt … too many times” in the past and now “would rather put their money into safer investments”. Moreover, “it would take decades to build new [nuclear] power stations” and electricity is no longer the sector of concern, given the rapid buildout of renewables, with attention having shifted to heating and transport.
Clean Energy Wire, CC BY-SA
Predictions that the nuclear exit would leave Germany forced to use more coal and facing rising prices and supply problems, meanwhile, have not transpired. In March 2023 – the month before the phaseout – the distribution of German electricity generation was 53% renewable, 25% coal, 17% gas, and 5% nuclear. In March 2024, it was 60% renewable, 24% coal, and 16% gas.
Overall, the past year has seen record renewable power production nationwide, a 60-year low in coal use, sizeable emissions cuts, and decreasing energy prices.
The country’s energy sector, it seems, has already moved on. In the words of one industry observer: “Once you switch off these nuclear power stations, they’re out.” And there’s no easy way back.
For better or worse, this technology – in its present form at least – is dead in the water here. For many Germans, it will not be missed.![]()
Trevelyan Wing, Fellow of the Cambridge Centre for Geopolitics and Centre Researcher at the Cambridge Centre for Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Governance (CEENRG), University of Cambridge
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.